Today we’ll be covering:
- Periodicity of physical properties of elements in Period 3
Let’s go!
What changes as you go across Period 3?
- the atomic number
- the number of electrons (& thus, valence electrons)
Trends in Physical Properties:
Property | Going across Period: | Why? |
Atomic Radius |  Decreases Decreases
| - Atomic charge increases
- Number of electrons in same principal quantum shell increases
- Shielding effect remains constant
- Greater attractive force
- Valence electrons are pulled closer to nucleus
|
Ionic Radius | 
- Decreases between Na+ & Si4+
- Increases between Si4+ & P3-
- Decreases between P3- & Cl–
- Ar does not form ion
| Between Na+ & Si4+: - Metals lose electrons to form cations
- They lose valence shell
- Ionic radius is much smaller than atomic radius
- Going across: higher nuclear charge pulls outer electrons closer
Between P3- & Cl–: - Non-metals gain electrons to form anions
- Valence shell contains more electrons than their atoms
- Larger repulsion between each valence electron
- Ionic radius is larger than atomic radius
- Going across: higher nuclear charge pulls outer electrons closer
|
Melting Point | 
- Increases between Na & Al
- Increases largely between Al & Si
- Decreases largely between Si & P
- Decreases between P & Ar
| Between Na & Al: - Bonding is metallic
- Structure is giant metallic
- Going across: more electrons are donated into sea of delocalized electrons
- Stronger forces of attraction
- More energy needed to overcome
Si: - Bonding is covalent
- Structure is giant covalent
- High energy is needed to break covalent bonds
Between P & Cl: - Bonding is covalent
- Structure is simple molecular
- Weak van der Waals’ forces require less energy to break compared to metallic bonds & covalent bonds
- Going across: structure of molecules changes
- Smaller the size, weaker VDW forces, lower melting point
- P: tetrahedral (large)
- S: puckered 8-membered ring (largest)
- Cl: diatomic (small)
- Ar: monoatomic (smallest)
|
Electrical Conductivity | 
- Increases between Na & Al
Decreases largely between Al & Si - Decreases between Si & S
- Cl & Ar do not conduct
| Between Na & Al: - Bonding is metallic
- Structure is giant metallic
- Going across: more electrons are donated into sea of delocalized electrons
- Higher conductivity
Between Si & S: - Bonding is covalent
- No delocalised free electrons
|
1st Ionisation Energy | 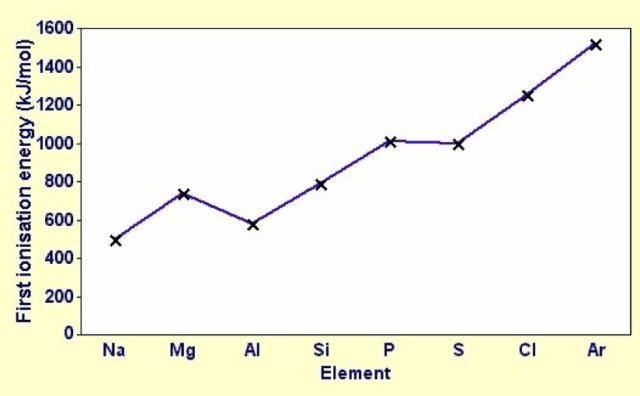
Increases, with small ‘dips’ | (See here for more in-depth explanations) - Positive nuclear charge increases
- Shielding effect is similar
- Effective nuclear charge increases
Dips are due to: - Electronic configuration (p-orbitals vs s-orbitals)
- Spin-pair repulsion (p1 vs p2)
|

 Decreases
Decreases



The radius of Ar is actually higher: this is because Ar has VDW forces, so the distance between atoms is larger (because of electron repulsion)
LikeLike